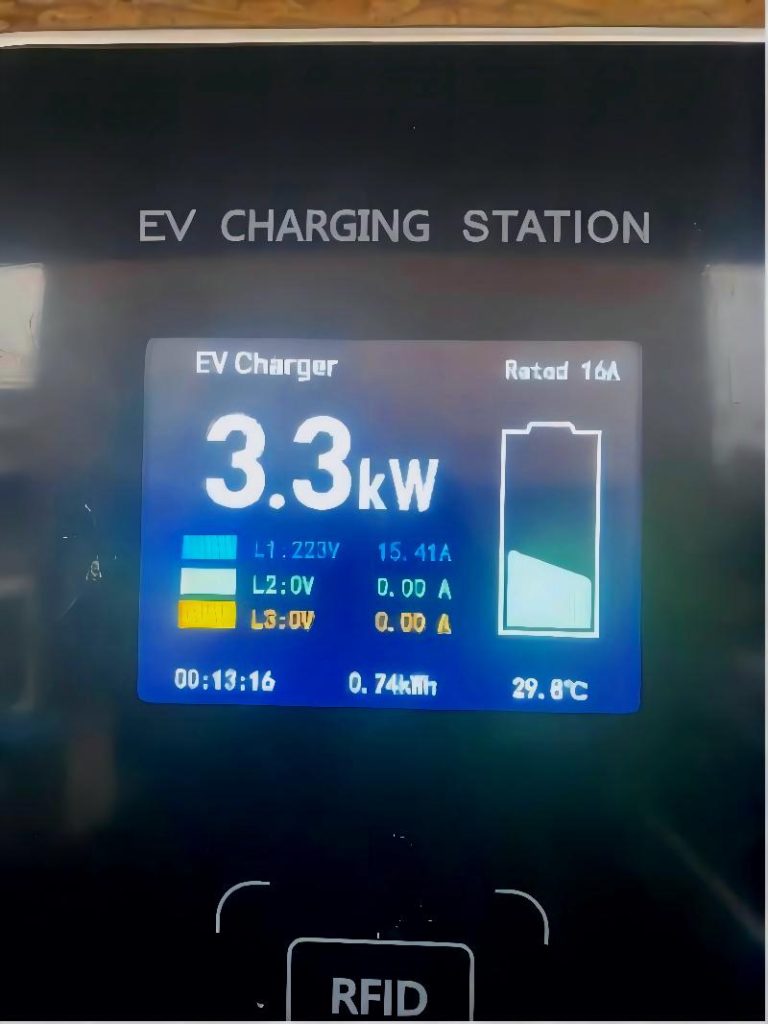
This is a case from a client of evseODM who ordered a batch of wallboxes with a rated charging power of 3.6kW. However, one end customer of this client complained that only 3.3kW of charging power was displayed on the wallbox screen during actual use which made our client very upset and he believed that our products had quality problems.
In fact, this is a very normal phenomenon.
This is a relatively common question. The main reasons for the deviation of power are as follows:
1.The electricity demand of the vehicle
The needs of the on-board charger decide how big the charging current will be. In order to protect the battery, some EV models will choose to charge at 90% of the rated charging power.
2. The battery is almost full
When the car battery is almost full, the charging current will be gradually reduced until it becomes a trickle to protect the car battery and prevent it from bulging, which is a normal protection mechanism that all car models have.
3.Power Loss
There will be a partial loss of energy during the charging process. For example, poor contact of the charging power supply terminal and excessive resistance (eg. when there are impurities on the contact surface) can both cause energy loss.
4.Measurement deviation
Any electronic device has measurement deviation more or less.
The above are several main reasons why the displayed charging power differs from the rated one. The rated charging power is the maximum power that the charger can deliver. However, this is not the actual power that you will see during use. The reason for this is because the rated power includes a margin of safety. This margin is necessary to prevent damage to your battery or overloading the charger.
So, what does this mean for you? It means that your charger is actually performing as it should. The displayed power during use is the true power output of the charger and is perfectly safe for your battery. There’s no need to worry about undercharging or overloading – your charger has got you covered.
Note: If the deviation is found to be significantly larger than the normal range, the specific cause needs to be further investigated.





